Organizations that embrace collaborative networks experience remarkable acceleration in growth and innovation. According to Innosabi, companies with strong partner ecosystems grow 5 times faster than those without, while 76% of executives consider partnerships essential for achieving their revenue goals. This dramatic difference reflects a fundamental shift in how modern enterprises create value.
Partner ecosystems are networks of businesses and service providers collaborating to create value, innovate, and expand market reach. Unlike traditional bilateral relationships, these networks consist of multiple interconnected partnerships working toward shared objectives, leveraging complementary strengths, technology, and expertise.
Traditional partnerships typically involve straightforward arrangements between two parties. A software company might work with a single reseller to distribute its product. Partner ecosystems operate differently. They encompass resellers, technology integrators, consultants, and sometimes competitors who collaborate to deliver comprehensive customer solutions.
Microsoft Azure exemplifies successful ecosystem architecture. Microsoft has built a massive partnership network including cloud service providers, software developers, and enterprise technology companies. Through alliances with businesses like SAP, Adobe, and VMware, Azure provides integrations enhancing cloud computing, AI, and cybersecurity capabilities.
Microsoft and SAP's collaboration enable enterprises to run SAP applications on Azure, providing improved scalability and security. Adobe's integration with Azure enhances digital experiences through AI-driven insights and cloud storage. These strategic partnerships help businesses streamline operations while allowing Microsoft to expand across multiple industries.
Different partner types collaborate to create value. Each participant holds a unique role in ensuring ecosystem success, contributing expertise, resources, or technology:
These diverse roles form the foundation of a healthy ecosystem. With the right group of participants in place, organizations can shift from simply managing individual partnerships to building a coordinated network that drives mutual growth. The next step is to develop a structured strategy that aligns these participants around shared goals and turns potential into performance.
Without structured approaches, partnerships become fragmented, leading to inefficiencies and missed opportunities. Strong ecosystem strategy ensures all stakeholders align, creating frameworks for sustainable business growth and collaboration.
Effective strategy should directly support overarching goals, whether expanding into new markets, enhancing customer experiences, or driving revenue advancement. Organizations must clearly define how partnerships contribute to measurable outcomes.
Partners need persuasive reasons to participate. These might include access to new customer segments, co-branding opportunities, or integration with industry-leading technology. As per a KPMG Survey, 75% of business leaders acknowledge ecosystem partnerships as a key driver of their growth strategies, reflecting the strategic importance organizations place on collaborative relationships.
Successful ecosystems define clear collaboration frameworks:
Platform thinking represents a fundamental shift in business strategy. Rather than focusing solely on delivering individual products or services, companies design platforms that serve as shared infrastructure, enabling partners, developers, customers, and other stakeholders to co-create value collaboratively.
Platform-driven companies often achieve significantly higher valuations. As per Adventis, platform companies commanded an 8.2x revenue multiple compared to 3.9x for traditional SaaS companies, demonstrating a more than 2x premium and showcasing the financial impact of ecosystem thinking.
Organizations can develop four distinct platform types:
Businesses investing in robust partner ecosystems gain significant competitive advantages. Partnerships enable faster innovation and efficient entry into new markets. Access to new technologies and specialized knowledge enhances product offerings and operational efficiency.
The speed advantage proves particularly valuable in fast-moving markets where first-mover benefits determine long-term success. Partner ecosystems allow organizations to simultaneously pursue multiple opportunities without diluting internal focus or exhausting resources. This parallel execution model dramatically shortens time-to-market for new offerings.
Integrating complementary services creates seamless, value-driven experiences. Companies with strong ecosystems experience faster revenue growth and improved profitability. Well-established networks foster credibility and thought leadership within industries.
According to Business Research Insights, the global partner ecosystem platforms software market is valued at USD 5.89 billion in 2025, expected to rise to USD 6.39 billion in 2026, and projected to reach nearly USD 11.81 billion by 2034, demonstrating massive market momentum behind ecosystem management solutions.
This market growth reflects widespread recognition that ecosystem management requires sophisticated tooling. Manual coordination suffices for small partner networks but becomes untenable as ecosystems scale. Platforms that automate onboarding, track performance, facilitate communication, and manage complex revenue-sharing arrangements have become essential infrastructure for ecosystem-led organizations.
Risk distribution represents another significant benefit. Diversified partner networks reduce dependence on single channels or technologies. When market conditions shift, ecosystems can adapt by emphasizing different partners or collaboration models without fundamental restructuring.
While benefits prove substantial, businesses often face operational and strategic hurdles. Without shared objectives, partnerships become misaligned. Keeping all partners engaged requires clear documentation and collaboration tools.
Misalignment often results from poor communication during partnership formation. Organizations must invest time articulating expectations, success metrics, and decision-making processes before formal collaboration begins. These foundational discussions prevent conflicts that arise when partners discover incompatible assumptions or conflicting priorities.
Managing data across multiple partners presents complexity, requiring centralized reporting solutions. Growing ecosystems demand structured management processes and digital tools. Maintaining partner motivation and alignment with long-term objectives requires continuous support and incentive structures.
Organizations must invest upfront in infrastructure, both technological and organizational. This includes platforms for data sharing, collaboration tools, and dedicated teams managing partner relationships. Underinvestment in ecosystem infrastructure leads to friction that frustrates partners and limits growth potential.
Cultural resistance within organizations can impede ecosystem development. Employees accustomed to controlling entire value chains may resist partnerships that require sharing control and credit. Leadership must actively promote collaborative mindsets and reward behaviors that strengthen ecosystem relationships.
Constructing strong partner networks follows a systematic process requiring careful planning and execution.
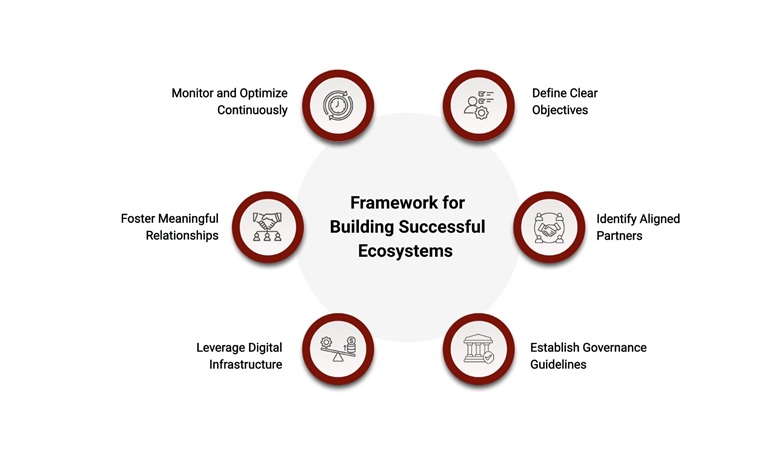
Outline specific achievements, whether market expansion, product enhancement, or operational efficiency. Measurable goals provide direction and enable performance tracking. Objectives should balance ambition with realism, stretching organizational capabilities without setting unattainable targets that demoralize participants.
Effective objectives specify timeframes and success criteria. Vague aspirations like "improve partnerships" provide insufficient guidance. Concrete goals like "expand into three new geographic markets through local partners within 18 months" create accountability and focus resource allocation.
Establish criteria for selecting partners to match your objectives. Consider technological compatibility, market reach, and expertise. Strategic alignment proves more valuable than sheer partner numbers.
Quality matters more than quantity in ecosystem development. Ten deeply engaged partners who share strategic vision deliver greater value than fifty superficial relationships. Rigorous partner selection prevents dilution of effort and maintains ecosystem coherence.
Due diligence extends beyond financial stability and market position. Cultural compatibility influences partnership longevity as much as business logic. Organizations should assess whether potential partners share values around customer service, innovation, and ethical business practices.
Define structured agreements, roles, responsibilities, revenue-sharing models, and performance expectations to avoid conflicts. Clear governance frameworks prevent misunderstandings and maintain productive relationships.
Governance structures should scale with ecosystem complexity. Simple partnerships might require only basic contracts and periodic reviews. Extensive ecosystems with multiple partner types need comprehensive frameworks addressing dispute resolution, intellectual property rights, data handling, and performance management.
Platforms and automation tools streamline partner management, ensuring smooth onboarding, communication, and performance tracking. Technology enables scalability while maintaining relationship quality.
Modern ecosystem management platforms provide centralized visibility into partner activities, automate routine administrative tasks, and facilitate knowledge sharing. These tools free relationship managers to focus on strategic initiatives rather than operational minutiae.
Invest in relationship-building through regular check-ins, joint initiatives, and co-marketing opportunities to maintain long-term engagement. Personal connections strengthen business ties.
Successful ecosystems blend transactional efficiency with human connection. While technology enables coordination, relationships ultimately depend on trust built through consistent communication and mutual support. Organizations should create opportunities for partners to interact both formally and informally.
Partner ecosystems remain dynamic. Continuously assess performance, gather feedback, and adjust strategies for sustained success. Regular evaluation identifies improvement opportunities and emerging challenges.
Monitoring systems should track both quantitative metrics and qualitative feedback. Revenue and customer satisfaction numbers reveal outcomes, while partner sentiment surveys uncover underlying issues before they impact performance. Balanced scorecards provide comprehensive ecosystem health assessments.
Organizations must track meaningful metrics demonstrating ecosystem health and performance. Revenue attribution models help understand partnership contributions to overall business results. Co-sell metrics (measures of joint sales efforts) reveal collaboration effectiveness between direct sales teams and partners.
Partner engagement measurements indicate relationship strength and satisfaction levels. Time-to-productivity metrics show how quickly new partners generate value. Customer satisfaction scores across partner-delivered solutions reveal service quality consistency.
Leading organizations develop balanced scorecards tracking financial performance, partner satisfaction, customer outcomes, and innovation metrics. This holistic approach prevents overemphasis on any single dimension while providing early warning when problems emerge.
Regular assessment enables course corrections before minor issues become major problems. Successful organizations establish feedback mechanisms gathering input from all ecosystem participants, using insights to refine approaches continuously.
Benchmarking against industry standards helps organizations understand relative performance. While each ecosystem possesses unique characteristics, comparing metrics like partner retention rates, time-to-first revenue, and customer acquisition costs against peers reveals improvement opportunities.
Organizations embracing partner ecosystems position themselves for sustained competitive advantage. The combination of strategic alignment, platform thinking, and systematic execution creates powerful networks generating value exceeding what any single organization achieves alone.
Success requires commitment to collaboration, investment in enabling infrastructure, and willingness to share control while maintaining quality standards. Companies that master these elements build resilient, adaptive organizations capable of thriving amid constant market evolution.
The evidence proves compelling. Businesses with well-structured partner ecosystems demonstrate measurably superior business growth, customer satisfaction, and market resilience. As markets become increasingly interconnected and complex, collaborative approaches transition from optional to essential for long-term viability and prosperity.
The future belongs to organizations that recognize partnerships as strategic assets rather than tactical arrangements. Those that invest in ecosystem development today position themselves to capture disproportionate value as network effects compound over time. The question facing business leaders is no longer whether to build partner ecosystems but how quickly they can establish competitive positions within them.

CredBadge™ is a proprietary, secure, digital badging platform that provides for seamless authentication and verification of credentials across digital media worldwide.
CredBadge™ powered credentials ensure that professionals can showcase and verify their qualifications and credentials across all digital platforms, and at any time, across the planet.

Keep yourself informed on the latest updates and information about business strategy by subscribing to our newsletter.