In today's fast-paced and ever-changing business landscape, companies must continuously seek out new opportunities for growth in order to remain competitive and thrive. However, identifying the most promising avenues for expansion and weighing the associated risks can be a daunting challenge for any business leader. This is where the Ansoff Matrix comes in - a simple yet highly effective strategy framework that has helped countless organizations successfully navigate the complexities of business growth for over half a century.
Developed by applied mathematician and business manager H. Igor Ansoff in 1957, the Ansoff Matrix (also known as the Product/Market Expansion Grid) provides a structured approach for evaluating different growth strategies based on whether they involve new or existing products and markets. By examining the four distinct quadrants of the matrix - Market Penetration, Market Development, Product Development, and Diversification - decision makers can gain valuable insights into the potential risks and rewards associated with each option, enabling them to make more informed choices and allocate resources effectively.
In this article, we will take an in-depth look at the Ansoff Matrix and its applications in business strategy. We'll explore the key characteristics and considerations for each of the four growth strategies, discuss the benefits and challenges of using the Ansoff Matrix, and provide practical tips and examples for putting this powerful tool into action. Let's dive in!
At the heart of the Ansoff Matrix lie four distinct growth strategies, each defined by a unique combination of products and markets (existing or new). These strategies are:
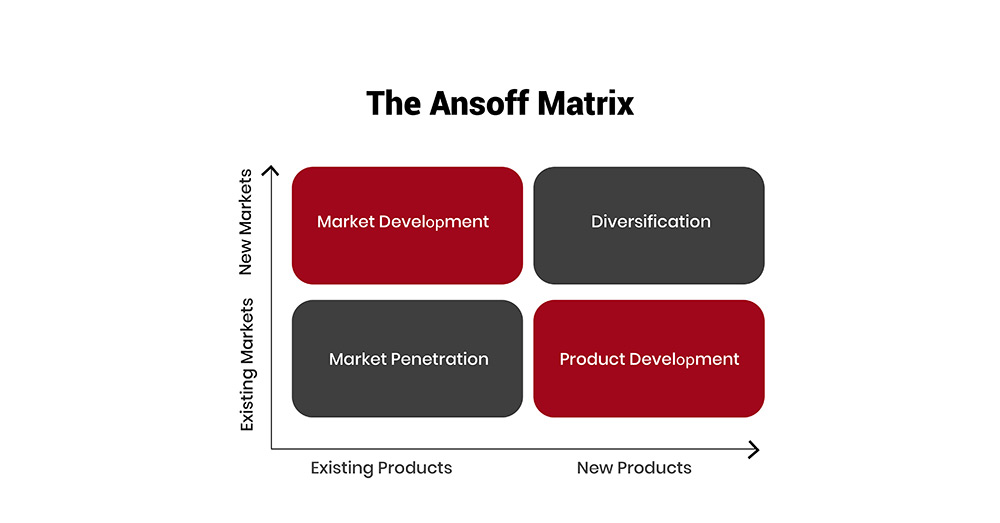
Let's take a closer look at each quadrant and the key considerations for pursuing growth within these areas.
The market penetration strategy focuses on increasing sales of existing products within existing markets. This approach is generally considered the least risky of the four options, as it leverages the company's established strengths and market knowledge. Typical tactics for achieving market penetration include:
For example, a consumer packaged goods company seeking to increase its share of the snack food market might invest in targeted advertising campaigns, introduce new packaging designs, or offer promotional discounts to drive sales of its existing product lineup.
The primary advantage of the market penetration strategy is that it allows businesses to capitalize on their current assets and capabilities, minimizing the need for substantial investments in new product development or market exploration. However, the potential for growth may be limited, particularly in mature or saturated markets where competition is fierce and opportunities for differentiation are scarce.
The market development strategy involves taking existing products into new markets, whether by targeting different customer segments, expanding into new geographic regions, or exploring alternative distribution channels. This approach enables companies to leverage their proven product offerings while tapping into fresh sources of demand. Common market development tactics include:
A classic example of successful market development is Apple's expansion into the Chinese market, where the company's iconic iPhone and iPad products have found a massive new customer base.
While market development can open up significant growth opportunities, it also comes with its own set of risks and challenges. Entering new markets often requires substantial investments in market research, localization, and infrastructure development, and companies may face intense competition from established players or cultural barriers to adoption.
Product development focuses on creating new products to serve your existing market. This strategy aims to leverage your brand's reputation and customer loyalty to introduce innovative offerings that address evolving customer needs or capitalize on emerging trends.
To implement a product development strategy, businesses should:
An example of product development is a smartphone manufacturer introducing a new model with advanced features to appeal to its loyal customer base.
Diversification is the riskiest of the four growth strategies, as it involves entering entirely new markets with new products. This strategy can be further divided into two types:
a. Related Diversification: Expanding into new markets or products that are related to your existing business, allowing for potential synergies in terms of resources, capabilities, or customer base. An example of related diversification is a car manufacturer expanding into the electric bicycle market, leveraging its expertise in vehicle design and manufacturing.
b. Unrelated Diversification: Venturing into markets or products that are unrelated to your current business, which can help mitigate risks associated with relying on a single market or product line. An example of unrelated diversification is a software company acquiring a chain of fitness centers to diversify its portfolio.
To pursue a diversification strategy, businesses should:
By carefully considering diversification opportunities through the lens of the Ansoff matrix, business leaders can make strategic decisions that drive growth while managing risk. The key is to find the right balance between leveraging existing strengths and exploring new opportunities in a way that aligns with the company's overall vision and goals.
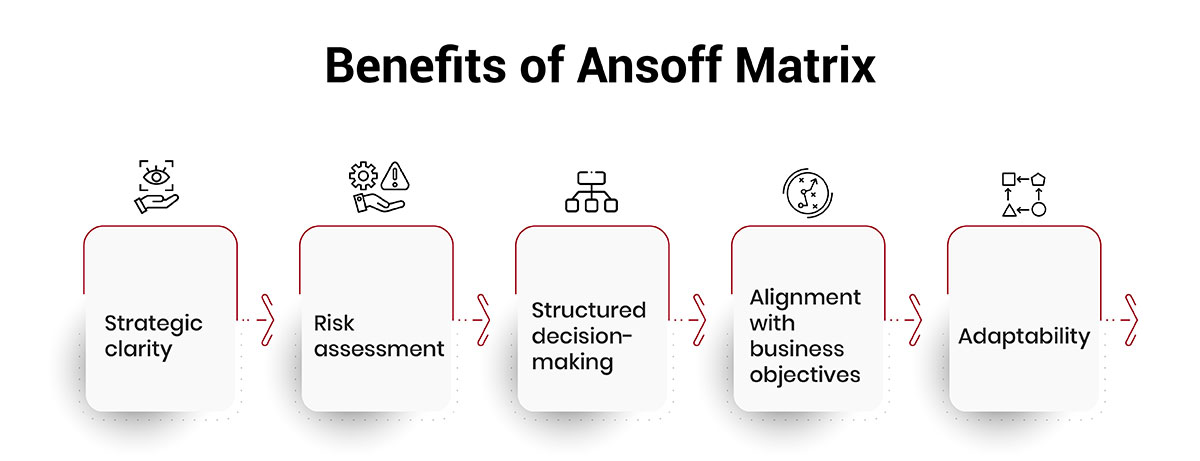
The Ansoff Matrix offers several key benefits for business leaders and organizations:
To effectively use the Ansoff Matrix in your business, follow these steps:

Here are some real-world examples of Ansoff Matrix application:
The Ansoff Matrix is a powerful strategy framework that helps business leaders evaluate and plan for growth. By considering market penetration, market development, product development, and diversification strategies, companies can make informed decisions about how to expand their business while managing risk.
Each growth strategy within the Ansoff Matrix comes with its own set of opportunities and challenges. Market penetration, the least risky option, focuses on increasing sales of existing products within current markets. Market development involves selling existing products in new markets, while product development introduces new products to existing markets. Diversification, the riskiest strategy, entails entering new markets with new products and can be further divided into related and unrelated diversification.
To effectively apply the Ansoff Matrix, businesses should assess their current situation, identify potential growth opportunities, evaluate risks and returns, prioritize strategies, develop an implementation plan, and continuously monitor and adapt their approach as needed.
Whether pursuing market penetration, market development, product development, or diversification, the key is to find the right balance between leveraging existing strengths and exploring new opportunities in a way that aligns with the company's overall vision and goals.

CredBadge™ is a proprietary, secure, digital badging platform that provides for seamless authentication and verification of credentials across digital media worldwide.
CredBadge™ powered credentials ensure that professionals can showcase and verify their qualifications and credentials across all digital platforms, and at any time, across the planet.

Keep yourself informed on the latest updates and information about business strategy by subscribing to our newsletter.